Each time a searcher clicks on the advert a charge is made to the advertiser, hence the term Pay Per Click or (PPC).
Friday, October 28, 2011
Cost Per Click & Pay Per Click
Each time a searcher clicks on the advert a charge is made to the advertiser, hence the term Pay Per Click or (PPC).
What is PPC Advertising?
Watch this intro. to Google AdWords Video & see text below
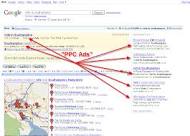
The listings shown by the Google are a mixture of so called Natural or Organic results and sponsored listings. The Pay Per Click Adverts are shown on the R.H.S. and sometimes also above the Natural listings.
How does PPC Advertising Work?
The reason the adverts appeared above when the search term "Widgets" was entered, by the searcher, was because they were programmed to do so by Google and the sponsor (the advertiser) . To help explain this, think of the actual advert as the part of an iceberg that you see above the water. We all know that there is more below the water! In this case think of there being a keyword container below the water. For this example this container certainly contains at least the one word "Widgets". It may however have many more keyword variations such as "Blue Widgets", "Cheap Widgets" etc.What is PPC Marketing
Pay per click (PPC) is an online advertising model used on search engines, advertising networks, and content websites, such as blogs, where advertisers only pay when a user actually clicks on an advertisement to visit the advertisers' website. Advertisers bid on keyword phrases relevant to their target market. When a user types a keyword query matching an advertiser's keyword list, or views a webpage with relevant content, the advertiser's ads may be displayed. Such ads are called a sponsored links or sponsored ads, and appear adjacent to or above the "natural" or organic results on search engine results pages, or anywhere a webmaster or blogger chooses on a content page.
Although many pay per click providers exist, Google AdWords, Yahoo! Search Marketing, and Microsoft adCenter are the largest network operators as of 2007. Minimum prices per click, often referred to as costs per click (CPC), vary depending on the search engine and the level of competition for a particular phrase or keyword list — with some CPCs as low as US $0.01. Very popular search terms can cost much more on popular search engines. The PPC advertising model is open to abuse through click fraud, although Google and other search engines have implemented automated systems to guard against abusive clicks by competitors or corrupt webmasters.
AdWords is Google's flagship advertising product and main source of revenue ($16.4 billion in 2007). AdWords offers pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and site-targeted advertising for both text and banner ads. The AdWords program includes local, national, and international distribution. Google's text advertisements are short, consisting of one title line and two content text lines. Image ads can be one of several different Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) standard sizes.
Yahoo! Search Marketing is a keyword-based "Pay per click" or "Sponsored search" Internet advertising service provided by Yahoo! Yahoo began offering this service after acquiring Overture Services, Inc. (formerly Goto.com). Goto.com was an Idealab spin off and was the first company to successfully provide a pay-for-placement search service following previous attempts that were not well received. Microsoft was the last of the "Big Three" search engines (Microsoft, Google and Yahoo!) to develop its own system for delivering pay per click (PPC) ads. Until the beginning of 2006, all of the ads displayed on the MSN search engine were supplied by Overture (and later Yahoo!). MSN collected a portion of the ad revenue in return for displaying Yahoo!'s ads on its search engine.
As search marketing grew, Microsoft began developing its own system, Microsoft adCenter, for selling PPC advertisements directly to advertisers. As the system was phased in, MSN search showed Yahoo! and Microsoft adCenter advertising in its search results. As of June 2006, the contract between Yahoo! and Microsoft has expired and Microsoft is displaying only ads from adCenter.
Although many pay per click providers exist, Google AdWords, Yahoo! Search Marketing, and Microsoft adCenter are the largest network operators as of 2007. Minimum prices per click, often referred to as costs per click (CPC), vary depending on the search engine and the level of competition for a particular phrase or keyword list — with some CPCs as low as US $0.01. Very popular search terms can cost much more on popular search engines. The PPC advertising model is open to abuse through click fraud, although Google and other search engines have implemented automated systems to guard against abusive clicks by competitors or corrupt webmasters.
AdWords is Google's flagship advertising product and main source of revenue ($16.4 billion in 2007). AdWords offers pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and site-targeted advertising for both text and banner ads. The AdWords program includes local, national, and international distribution. Google's text advertisements are short, consisting of one title line and two content text lines. Image ads can be one of several different Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) standard sizes.
Yahoo! Search Marketing is a keyword-based "Pay per click" or "Sponsored search" Internet advertising service provided by Yahoo! Yahoo began offering this service after acquiring Overture Services, Inc. (formerly Goto.com). Goto.com was an Idealab spin off and was the first company to successfully provide a pay-for-placement search service following previous attempts that were not well received. Microsoft was the last of the "Big Three" search engines (Microsoft, Google and Yahoo!) to develop its own system for delivering pay per click (PPC) ads. Until the beginning of 2006, all of the ads displayed on the MSN search engine were supplied by Overture (and later Yahoo!). MSN collected a portion of the ad revenue in return for displaying Yahoo!'s ads on its search engine.
As search marketing grew, Microsoft began developing its own system, Microsoft adCenter, for selling PPC advertisements directly to advertisers. As the system was phased in, MSN search showed Yahoo! and Microsoft adCenter advertising in its search results. As of June 2006, the contract between Yahoo! and Microsoft has expired and Microsoft is displaying only ads from adCenter.
What is PPC? Benefits to PPC
What is PPC ?
PPC stands for "pay per click". Pay per Click is an advertising model where businesses pay an agreed upon amount, each time their advertisement is "clicked", not each time their ad is displayed.
PPC stands for "pay per click". Pay per Click is an advertising model where businesses pay an agreed upon amount, each time their advertisement is "clicked", not each time their ad is displayed.
Advertisers typically setup ppc on a PPC network and define how much they are willing to spend for each click-through that they receive.
Advertisers select keywords, keyword phrases, keyword groups, or categories in which they want their advertisements to appear.
Benefits to PPC
When you setup a PPC campaign you can controlthe traffic. While a new website takes time to rank well in search engines, with PPC you can turn the traffic on and off. With PPC you can create almost instant traffic.
When you setup a PPC campaign you can controlthe traffic. While a new website takes time to rank well in search engines, with PPC you can turn the traffic on and off. With PPC you can create almost instant traffic.
Unlike organic search listings you control the information (ie. description) and where the visitor is directed on your website.
Another benefit to PPC listings is the opportunities for international exposure. Organic search listings vary in different geographical regions. With PPC you control where you are seen.
Another benefit to PPC listings is the opportunities for international exposure. Organic search listings vary in different geographical regions. With PPC you control where you are seen.
Click Fraud
Fraud has plagued PPC advertising medium since its inception, and while many PPC networks have made significant progress in combatting click fraud, it is still something to be cognizant of.
Fraud has plagued PPC advertising medium since its inception, and while many PPC networks have made significant progress in combatting click fraud, it is still something to be cognizant of.
Tracking PPC
In order to determine how effective a PPC campaign is, it is important to implement tracking. Just because an advertisement has a high number of click throughs does not mean it is the best ad. It is easy to get users to click on "Free Software" but few of those clicks will convert to sales.
In order to determine how effective a PPC campaign is, it is important to implement tracking. Just because an advertisement has a high number of click throughs does not mean it is the best ad. It is easy to get users to click on "Free Software" but few of those clicks will convert to sales.
Monitor, measure and maintain successful PPC campaigns.
PPC Management and Tracking Tools
PPC Management and Tracking Tools
The Goal of PPC
 A successful PPC campaign should be targeted not too narrowly and not too broadly. Direct the user to a relevant landing page that has a direct relationship to the keyword or phrase.
A successful PPC campaign should be targeted not too narrowly and not too broadly. Direct the user to a relevant landing page that has a direct relationship to the keyword or phrase.
List of PPC Search Engines
There are hundreds of Pay Per Click Search Engines you can buy traffic from.
There are hundreds of Pay Per Click Search Engines you can buy traffic from.
KeywordMaxKeyword service that gives you the detailed data you need to determine exactly how successful your pay-per-click ads are... so you can strengthen your ROI.
UK SMBs Struggle To See Value In AdWords
A new survey of roughly 500 small businesses (SMBs) in the UK reveals that only a minority perceive AdWords to be delivering a positive ROI. The online survey was conducted by Workbooks.com and YouGov. The question asked was: “Do your sales exceed the cost of AdWords?” Only 18 percent said “yes,” 45 percent said “no” and 37 percent were unsure.

This is not a new revelation. Google has a network of resellers promoting AdWords to small businesses. However the “churn” rates experienced by those programs often exceed 90 percent per year. The reasons for high churn are varied but boil down to the fact that these SMBs are having difficulty seeing value in many of these programs.
Google has recently built its own telesales force and a parallel customer service organization to onboard SMBs and help them better understand AdWords. Google also created AdWords Express (formerly Boost), which simplifies the process of adoption and outsources ongoing campaign management (to Google).
Most SMBs don’t have the time to become sophisticated enough about paid-search to really see the benefits that professional search marketers do. But there’s also some skepticism about the value of paid search as well. While they all want to rank or “show up at the top” of Google that desire often doesn’t extend to paid results.
The PR Plan For Publisher Backlash: It’s A Tiny Loss!
Google still knew there would be backlash from another group of publishers, those who have received this Caller ID referrer data from Google’s “free” or “organic” or “editorial” or “SEO” listings. What was the solution for that problem?
Here, Google seems to have a three-fold approach. First, suggest that only a tiny amount of data is being withheld. Some scoffed at Google’s estimate that I reported, that this would impact less than 10% of query data. But so far that seems to be holding true.
For example, here was our second most popular keyword sending us traffic from Google yesterday, according to Google Analytics:
“Not Provided” is what Google reports in cases when it now blocks referrers — or technically, it still provides referrers but is specifically stripping search terms out of them.
Our number two keyword! And yet, we received nearly 15,000 keyword-related visits from Google yesterday. These terms that were withheld amounted to only 2.6% of them.
On my personal blog, this is in about the 2% range. SEOmoz reported around 2%, as well.
These low figures will makes it easier for Google to gloss over publisher concer
ns, especially when they’re almost all being voiced by those in the SEO industry. The industry has a bad name, so if it’s against something, that can almost seem like a ringing endorsement for good.
Ars Technica had some comments like this, in response to its story on the Google change:
I’m playing the saddest song in the world on the smallest violin in the world. Poor, poor, SEO leaches
I AM completely unsympathetic. The sooner these SEO leeches, parasites, spammers and scammers die die die the better off the web will be.
Don’t make this mistake. This is not just an SEO issue. This is a user privacy issue. SEOs are simply the harbingers spotting Google’s hypocrisy around privacy.
Google Puts A Price On Privacy
Earlier this week, Google made a significant change purportedly to better protect the search privacy of users. In reality, it specifically — and deliberately — left a gaping hole open to benefit its bottom line. If you pay-to-play, Google will share its search data with you.
Google’s a big company that goes after revenue in a variety of ways some critics feel put users second. However, I’m struggling to think of other examples where Google has acted in such a crass, it’s all-about-the-revenue manner as it has this week. The best comparison I can think of is when Google decided to allow Chinese censorship. Yes, this is in the same league.
It’s in that league because Google is a company that prides itself by doing right by the user. Yet in this case, it seems perfectly happy to sell out privacy, if you’re an advertiser. That’s assuming you believe that Caller ID-like information that’s being blocked (except for advertisers) is a privacy issue.
Google doesn’t, as best I can tell. Instead, the blocking is a pesky side effect to a real privacy enhancement Google made, a side effect Google doesn’t seem to want to cure for anyone but advertisers.
If it had taken a more thoughtful approach, ironically, Google could have pushed many sites across the web to become more secure themselves. It missed that opportunity.
I’ll cover all of this below, in detail. It’s a long article. If you prefer a short summary, skip to the last two sections, “Why Not Get Everyone To Be Secure” and “Moving Forward.”
Default Encrypted Search Begins
Let’s talk particulars. On Tuesday, Google announced that by default, it would encrypt the search sessions of anyone signed in to Google.com. This means that when someone searches, no one can see the results that Google is sending back to them.
That’s good. Just as you might want your Gmail account encrypted, so that no one can see what you’re emailing, so you also may want the search results that Google is communicated back to you to be kept private.
That’s especially so because those search results are getting more personalized and potentially could be hacked. The EFF, in its post about Google’s change, pointed to two papers (here and here) about this.
Encryption Can Break Caller ID
There’s a side effect to encryption that involves what are called “referrers.” When someone clicks on a link from one web site that leads to another, most browsers pass along referrer data, which is sort of like a Caller ID for the internet. The destination web site can see where the person came from.
When someone comes from an encrypted site, this referrer information isn’t passed on unless they are going to another encrypted site. That means when Google moved to encrypted search, it was blocking this Caller ID on its end for virtually all the sites that it lists, since most of them don’t run encrypted or “secure” servers themselves.
This is a crucial point. Encryption — providing a secure web site — doesn’t block referrers if someone goes from one secure web site to another. Consider it like this:
Unsecure >>> passes referrer to >>> Unsecure
Secure >>> passes referrer to >>> Secure
Secure /// does NOT pass referrer to /// Unsecure
Google Introduces “Bid For Calls” On The PC
Earlier this summer Google gave an indication this was coming. Now Google is rolling out what it’s calling “bid for calls,” a pay per call (PPCall) offering on the PC. This is distinct from Click to Call, its successful mobile PPCall product. The program will launch in the US and UK at first and relies on the Call Metrics (Google Voice) infrastructure.
AdWords advertisers must use Call Metrics and a Google Voice-generated call tracking number to participate. But rather than just paying $1 per completed call for call tracking, advertisers can now separately bid on calls.

In the near future, depending on the amount of bids and how many calls are received, Google will begin to include calls in its ads quality score. I spoke to Google’s Surojit Chatterjee who told me advertisers that don’t participate in bid for calls won’t be disadvantaged. But advertisers whose paid-search ads are generating lots of calls may see a boost in their AdWords rankings accordingly.
In other words, “call-through rate” will now be a factor in ranking. To participate in bid for calls advertisers enable Call Extensions and Call Metrics:

Last year when Google’s call tracking program “Call Metrics” was first introduced I suspectedPPCall wouldn’t be far behind. Google experimented with PPCall on the PC years ago but never rolled it out broadly.
Despite its relatively low-key introduction this morning, this is a major development for Google and for AdWords advertisers. Being able to bid on calls separately as well as getting ranking “credit” for calls generated from Google ads will be significant for many advertisers (local and national) that operate call centers or have stores in the real world.
What Is PPC, CPC & Paid Search Marketing?
Some people also refer to paid search as SEM, through here at Search Engine Land, we consider SEM (search engine marketing) to be an umbrella term that encompasses both paid search and SEO (search engine optimization).
Advice For Newbies
New to paid search ads? Don’t worry! Search Engine Land has the perfect series for you: PPC Academy. This special column began in 2010 and provides a different installment each week to bring you up to speed on paid search.
Another starting place is Google’s “Insider’s Guide To AdWords,” which you’ll find here in PDF format. AdWords is by many measures the most popular paid search platform used by search marketers, so the guide offers a useful introduction.
Of course, there’s much more to paid search than what’s covered in Google’s guide. You might consider some of the many print books out there with advice. Here’s our review of some newer books: A Roundup Of Best Search Advertising Books.
Advice At Search Engine Land
Here at Search Engine Land, we provide paid search advertising information and news in a variety of ways:
Paid Search is Search Engine Land’s column that covers different paid search topics every week.
Checklist of Current SEO Techniques
Search engine optimization entail fine tuning a website’s code alongside a thorough linking architecture and just like mechanics, use a checklist to track down what has already been accomplished and how to measure the effect of each step on all other variables. The following is a basic overview of the steps you should take to ensure you leave nothing to chance, anything that can have a positive effect on your website’s ranking thus improve the amount of traffic.
Before you start any SEO marketing campaign, it is highly recommended that you have a point of reference to ensure all avenues are explored fully. Webmasters should disregard most of the information they get when listing their services because majority of the procedures these listing companies describe are either ineffective or unnecessary. For instance, submitting a domain name to search engines has become ineffective because today website spidering comes automatic, at least in Google. There is even reason to believe that even using a submission tool can lead to ‘sandboxing’ a situation where your website is put on probation and becomes invisible in the SERPs for a given period of time.
If you are serious about making a living off your business through search engine traffic, you should oversee the building of your website and ensure it is done correctly. Here is a checklist that should act as your point of reference mainly for purposes of comparing techniques.
Of course there are numerous other ideas to develop and many other tasks to perform but if the above-listed checklist is followed well, you can rest assured that your website is ready to create an impact online. But when all is said and done, the main factor you should consider is the quality of content that you create. A website that has quality informative and interesting content will be deserving of major attention and perceived as an authority website in the market niche. Anchor text links basically outline the path to the source of any content and when the total number of links in your website continues to multiply constantly through downloads, rest assured traffic will come in huge growing numbers, which of course translates to business.
Before you start any SEO marketing campaign, it is highly recommended that you have a point of reference to ensure all avenues are explored fully. Webmasters should disregard most of the information they get when listing their services because majority of the procedures these listing companies describe are either ineffective or unnecessary. For instance, submitting a domain name to search engines has become ineffective because today website spidering comes automatic, at least in Google. There is even reason to believe that even using a submission tool can lead to ‘sandboxing’ a situation where your website is put on probation and becomes invisible in the SERPs for a given period of time.
If you are serious about making a living off your business through search engine traffic, you should oversee the building of your website and ensure it is done correctly. Here is a checklist that should act as your point of reference mainly for purposes of comparing techniques.
- Include all keywords in your JavaScript file in HMTL comment tags
- Have an XML sitemap within your site
- Name your site’s URL using the same keywords as they appear on your webpage but separated using a dash
- Your keywords should feature in the meta description, titles, file names of your images, header tags, and alt tags of images
- Make manual submission for listing to at least 250 search engine optimized directories
- Retain a 3-7% keyword density
- Conduct an organic keyword research using software such as Web CEO
- Each page ought to have only one <h1> tag, and also make use of tags 2,3,4
- Reduce code and increase content for purposes of high text ratio
- Reduce your webpage’s loading time
- If your URLs are dynamic, ensure they are translated into HTML
- Ensure your website is W3C compliant
- Use anchor text to link keywords in articles to other articles within the same site
Of course there are numerous other ideas to develop and many other tasks to perform but if the above-listed checklist is followed well, you can rest assured that your website is ready to create an impact online. But when all is said and done, the main factor you should consider is the quality of content that you create. A website that has quality informative and interesting content will be deserving of major attention and perceived as an authority website in the market niche. Anchor text links basically outline the path to the source of any content and when the total number of links in your website continues to multiply constantly through downloads, rest assured traffic will come in huge growing numbers, which of course translates to business.
Thursday, October 27, 2011
How to Optimize Your Online Content
Obviously, as with any search engine optimization strategy, content optimization is not a plug-and-play technique. However, there are certain things that need to be observed, regardless of your website and your industry’s or niche’s landscape and competition. The following techniques will thus help you properly optimize your content while ensuring that you work on these as early as possible (as mentioned above, I will however not be considering keyword density, which most people already know about and which is already causing a debate).
Content length and quality are becoming increasingly important as evidenced by the Google Panda updates which have wiped out many websites’ visibility and even led to several online businesses shutting down. Content length and quality do not necessarily go together since this you can have a short article that is nevertheless of very high quality but I will be grouping them together for the purpose of this article.
Content quality is obviously a rather general term as we all interpret quality differently. However, the one crucial thing is that it should be unique content. Duplicate content is always a no-no and should be avoided at all costs. Poorly written content is also something you must always avoid. While it may be possible to fool search engines with such content, your readers will notice, which will result in visitors leaving your website a mere 5 seconds after reaching it.
As far as content length is concerned, an article should typically consist of at least 400 to 450 words. Longer is obviously better although it may not be a sensible idea to have a single 2000-word article. Some people have argued that it is a good idea to mix up the longer articles with shorter ones that barely exceed the minimum 400 words. However, this is hardly logical. In fact, you are much better having moderately lengthy articles all the time, since this allows you to target more long tail keywords.
Content layout
Another often forgotten factor of online content optimization is the fact that how your content is display is also crucial. Keep in mind that the online medium comes with its own rules. Moreover, with so many people now using mobile devices to browse the web, it becomes even more important to understand how to optimize your content layout.
Since your content should now be leaning towards the longer side, your use of paragraphs and headers become strategies you must always pay attention to. Your paragraphs should thus consist of at around four to six sentences, although this depends greatly on your general website layout. If you have an extremely narrow layout for your main content, you will obviously be restricted to fewer sentences per paragraph. However, keep in mind that two-sentence paragraphs can be annoying when you choose your ideal sentence count.
Better Results Of Internet Marketing Campaigns
Oct
Contributions Of Internet Marketing
Internet marketing can surely be regarded as one of the strongest forces pushing the evolution of internet to ever new horizons. In fact, web gurus regard internet marketing services so much, because it is serving as a domain that not only contributes for its own growth and development, but for the evolution of internet as a whole.
SEO and PPC
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and PPC (Pay-per-Click campaign) have been the most influential tools at the hands of web marketing. Though different in rules and regulations, both of these disciplines serve for effective online promotion.
SEO and PPC can play together to be the best of allies for online promotion of your site, so can they create havoc for you, if handled unwisely. In this regard, your PPC advertising department can help your SEO department by making sure their paid search campaign essential testing is done in a manner that it does not affect your site’s organic rankings.
Search Engine Bots
Such a confusing situation can arise because of improper handling of “search engine bots”, mostly by PPC department while testing their landing pages for better results of paid searches. “Search engine bot” basically refers to a computer program that search engines use to crawl and index web pages all through the virtual world.
This crawling is no random crawling; it follows strict rules and regulations communicated to it through an instruction manual in form of a file known as “robots.txt”. Through the instructions confined in this file a search engine bot comes to know what to crawl and what not to crawl on a particular site.
Your search rankings can be affected quite severely due to an improperly configured robots.txt file. It can cause:
Lower the results of your organic rankings
Prevent your ads from being approved
Deplete your site’s quality scores
Ignite a variety of other problems
To stay safe from such issues, it is better to know the behavior and approach of some of the most common search engine bots, not only helpful for SEO specialist, but also equally help for PPC consultants.
Google AdWords Robot
Google relies on a bot referred as “adsbot-Google” for crawling through URLs with the intent of quality scoring purposes. Google’s bot follows a distinct set of rules for crawling through web pages as compared to other search engine bots, and interprets robots.txt file in a different manner. Almost all other bots observe a global disallow, meaning that they do not go through every page for crawling. Google’s bot, on the other hand, does not heed to global disallow and goes through every single page of a website. However, if your robots.txt file specifically calls upon a bot, then adsbot-Google will strictly follow your instructions whether to crawl or not crawl a specific page.
Microsoft also resorts to a special type of bot for approval purposes, referred as “adidxbot” or “MSNPTC/1.0”. It follows the standard bot conventions and fails to crawl through a page when sees a global disallow on it, thus generating various ads approval issues.
Webmaster Center
The bot Bing relies on is referred as “Webmaster Center”, but it lacks any effective mechanism to check whether your site specifically blocks their ads bot.
Testing Landing Pages
From PPC’s perspective, testing of a landing page is very critical for success of a PPC campaign. PPC experts often end up creating different versions of the same page hosting different page layouts, headlines, buttons, etc, while most of the content remains same on all the pages.
If PPC experts are not acquainted with effective usage of blocking or allowing search engine bots to crawl through specific pages, they might end up damaging organic search rankings of the site for issues like duplication of content and so forth.
Conclusion
Importance of Backlinks and their Quality
One of the most important aspects of SEO is the backlinks. However, there is something even more important than backlinks – their quality. Most people don’t really understand that the number of links you have pointing to your website almost doesn’t matter if the links are not what they should be.
Page Rank – Having a link pointing to your website from a website with a high page rank is great and adds value to the link. For example, a couple of links from a high PR websites have a lot more value than a hundred links from websites with no PR at all.
Domain Authority – Looking for a high page rank is simply not enough. High PR websites with no domain authority are good but not nearly as good as high PR websites with a high domain authority. Getting links from such websites will pass way more link juice and value to yours.
DoFollow – There are two major types of links – NoFollow and DoFollow. When the link is DoFollow, it basically means that it passes link juice to your website. If the attribute is NoFollow, you are not getting anything from that type of links and most people say they are useless. However, some people say that the statement that NoFollow links are not passing link juice and are a waste of time is a myth. Although nobody knows the truth for sure, I believe NoFollow links are not useless at all if they are coming from websites with a high page rank and domain authority.
Niche related – Getting a link from a diving website when you are a carpenter is not a good idea. Even if the diving website has a high PR and DA, it is not related to yours in any way and the value of the link you will get from it will drop drastically. Also getting a link from another carpenter’s website and linking back to him is pointless since he is your competition. However, getting a link from a website that offers wood supplies, has a high PR and DA and offers DoFollow links is great. This website is not your direct competition and is related to your niche so you should go for it.
Panda 2.0: Google Rolls Out Panda Update Internationally
Live for All English Queries
The original algorithm update impacted only U.S. queries. As of today, this change is live for all English queries worldwide. This includes both English speaking countries (such as searches on google.co.uk, and google.com.au) and English queries in non-English countries (for instance, for a searcher using google.fr who’s chosen English-language results).
In the United States, the initial launch impacted nearly 12% of queries, so it stands to reason that the impact may be similar for English-speaking searchers across the world.
Incorporating Searcher Data About Blocked Sites
Google has always used a number of signals in determining relevant search results. Some of these are on the pages themselves (such as the text on a page), some are on other sites (such as anchor text in links to a page), and some are based on user behavior (for instance, Google gathers data about how long pages take to load by using toolbar data from users who access those pages).
In recent months, Google has launched two ways for searchers to block particular sites from their search results. The first was a Chrome extension. More recently, Google has launched a block link directly in the search results that appears once a searcher has clicked from the results to a site and then return to the search results.
Now, they are using data about what searchers have blocked in “high confidence situations”. Google tells me this is a secondary, rather than primary factor. If the site fits the overall pattern that this algorithm targets, searcher blocking behavior may be used as confirmation.
Impact Seen To a Wider Variety of Sites
In the initial launch, large sites were primarily affected. This makes sense as larger sites, with more pages, traffic, and links, have more signals available. With the latest update, smaller sites may see an impact. Amit Singhal, in charge of search quality at Google, notes in the blog post, “this change also goes deeper into the “long tail” of low-quality websites to return higher-quality results where the algorithm might not have been able to make an assessment before”.
Amit Singhal told me,
“We’re focused on showing users the highest quality, most relevant pages on the web. We’re cautious not to roll out changes until we’re confident that they improve the user experience, while at the same time helping the broader web ecosystem. We incorporate new signals into our algorithm only after extensive testing, once we’ve concluded that they improve quality for our users.”
Best On-Page Search Engine Optimization Tips
Though there has been a lot of discussion lately about how important it is to have solid off-page search engine optimization, like social media, it’s also vital that you remember the basic principle of a search engine algorithm. It’s trying to find relevant pages to a search query based on the content on the page. Your goal for on-page search engine optimization is to make your page appear to be more relevant than any other page for your selected keyword.
LSI Keywords
One way a search engine can tell if a page is relevant is to look for synonyms of terms searched for. If a page features these synonyms several times throughout the article, it’s less likely to be a keyword-stuffed, irrelevant article. You can promote the relevancy of your page by including LSI keywords, or words you might find in a thesaurus when you search for your keyword, as often as possible.
Domain Name Keyword Targeting
You can target a keyword directly by using your page’s URL. Before designing a new site, decide what keywords will be important for your early targeting efforts and place one or two in the domain name of your site. Sometimes you can separate a domain name with a hyphen for uniqueness and readability, like, sandiego-lawyer.com, but try not to use two or more hyphens, as that starts to look like spam.
Title and Header Tags
Another way a search engine determines the relevancy of a page is by seeing what keywords are featured in the page’s title and header tags. The reason a search engine specifically looks at these tags is because these are the tags a user is most likely to look at while skimming a page. Since the header tags are summaries of paragraphs, they are like condensed phrases of information, and looking at the header tags saves the effort of having a machine try to discern what a paragraph is about.
Meta Description
Don’t forget to include meta descriptions featuring your keywords, as search engines do use meta descriptions to decide what queries a page is relevant to (but not meta keywords: they ignore these).
Internal Cross-Linking
Your page’s navigation should be easy to use and provide links to all relevant areas of your site. No page on your site should ever be more than two or three clicks away from any other page. Cross-linking helps share your search engine optimization results across other pages on your site, rather than promoting a section of your site, like your blog, at the cost of other sections, like your products.
Use a Sitemap
Creating and uploading a sitemap to Google is easier now than ever, so if you’re not already utilizing a sitemap, this should be the first thing on your list. If you do use a sitemap, make sure it is getting updated automatically by your Content Management System on a regular basis.
Image Alt Tags
You should be using alt tags for all of your images, describing what the image is. You should also be using image filenames to stuff additional keywords whenever possible. Your alt tags and filenames will most influence your Google Images SEO, which can bring a few additional hits to your site.
Keyword Density
The tried and true search engine optimization technique, using a keyword density of around 4-5% seems to be the sweet spot these days. Using 8%+ is going to make you subject to a Google penalty and therefore devalue your page in the search engine results.
Even if you’ve worked on your on-page search engine optimization in the past, this article makes a good refresher course for the things you should be doing on a regular basis, like checking your sitemap, making sure your newly-uploaded images are alt-tagged, and maintaining a consistent keyword density across your site. Remember that these factors change from update to update, sometimes several times a year, so it’s important to keep emerging SEO trends in your peripheral vision, even while you improve your on-site SEO.
Posted by Greg Henderson, an Internet Marketer and SEO Associate for an email search and free public records site: MFES & RecordsProject. Please feel free to leave a comment or email him.
Keys to Understanding Google Panda
What is Google Panda?
If you’re involved in the search engine niche, you’ve heard of Google Panda. If you’re not, you probably just clicked this article because you think pandas are adorable. In either case, you’re already being affected by changes to Google’s search engine codenamed “Google Panda.”
The Skinny on Search Updates
Several years ago, the quality of search engines results started to noticeably decline. A lot of the results were sites that usually offered little informational value – like EzineArticles or eHow – or sometimes no informational value at all, just worthless content that was written by a computer and unreadable or simply plagiarized another site like Wikipedia.
Google took action, making three major changes to its search engine algorithm since Feb. 24, 2011. The first, Panda 1.0, targeted thin or shallow content, downgrading the search engine rankings of major content farms like About.com and EzineArticles. About 12% of all websites were affected by this change, most noticeably large sites that got downgraded and small sites that got a boost. The second algorithm update, Panda 2.0, was implemented on April 11, expanding the Google Panda algorithm, which was previously U.S. only, to the rest of the English language results on Google. Since then, bi-weekly updates of the Panda algorithm has brought us to Panda 2.5 which has included additional signals that Google uses to differentiate between high-quality and low-quality sites.
Why Businesses Need Professional Web Design
Having an Internet presence is very important these days. Your customers need to be able to find you as easily as typing in your company name into a toolbar, or a quick Google search. However, if you are on the Internet, you need a professional looking website. Even if you have to pay, your business needs to look as if drawing in customers matters.
Professionalism Matters In Business
Business demands that you be a professional at all times when dealing with customers, or trying to attract new ones. Those who cannot look and act professional will not be valued by customers. How would you like it if you went to a company website only to find out it was an old MySpace Blog that hadn’t been updated in years? It would probably turn you off to the company.
Your website is part of your marketing campaign. If you don’t know how to market, or cannot market well, you are going to be behind the eight ball from the start. However, if you allow other professionals to help you grow and market your company, it can really help it thrive in the long run.
SEO Is Important
A professional website designer is going to know how to maximize your website for optimal traffic and targeted traffic. Paying for these services will certainly give you a return on your investment. While SEO can be tricky even for a professional, that person will know more about different techniques that can be used to maximize your traffic. At very worst, you are going to save yourself a lot of time and frustration trying to maximize your site.
You Have A Business To Run
If you are considering making a website for your business, it would be a good idea to hire a professional to do that for you. It might cost the company some money, but it will be worth it. When the customers start rolling in because you have a sharp, SEO driven website, the company will grow and make more money. It will be a smart investment that will allow you to spend more time on your product and not on your website.
Google +1 latest Update
Google has introduced a new feature in its suite of social search services — the +1 button. Similar to Facebook’s ubiquitous Like Button, the +1 enables users to exchange recommendations within Google’s search results. Eventually users will also be able to “+1” on sites across the web.

Like Facebook’s Like Button or Twitter’s ‘Tweet This’ button, which have quickly spread across the Internet, Google’s +1 seeks to employ a user’s social graph to improve their search experience, making it quicker and more personal. As Rob Spiro, Product Manager, writes in Google’s blog post introducing the service, “The beauty of +1′s is their relevance — you get the right recommendations (because they come from people who matter to you), at the right time
(when you are actually looking for information about that topic) and in the right format (your search results).”
Google’s recent launches of Buzz and now the +1 feature highlights the growing interconnection between search and social, and the increased role that relationship will play in integrated marketing strategies. As Mike Jarvinen, VP Marketing Strategy at The Search Agency, explains, “Coming to your local webpage: ‘Tweet This, Like This or +1 This.’ It makes sense that Google would get in the game – it will it provide the same type of open graph over time that Facebook and Twitter have made ubiquitous. By allowing that integration directly in SEM ads and SEO results with potential signals of helping rankings (won’t help quality score for ads yet but who knows about the future), there is potential to make a big splash in not only how we think about search but also how we think about truly integrated marketing with search at its center.”
In addition, marketers will have a new source of data to gauge the effectiveness of ad copy and web content. As Josh Peters, Social Media Manager at The Search Agency, explains, ” With the +1 feature, webmasters (via Google Webmaster Tools) will be able to see how many times their pages are +1’d and advertisers will be able to see what ads get +1’d as well. An altruistic view of this is that we will be able to know which content is liked more and thus as content creators and advertisers we can make better and better content and targeted ads. I think the full breadth of this has yet to be envisioned, but with all the updates Google has done recently to social search and Google Profiles it looks like bigger things are in the works.”
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
